**Warts Unveiled: Understanding, Treating, and Preventing the Common Skin Growth**
Warts, those pesky skin growths that seem to appear out of nowhere, are a common dermatological condition that affects people of all ages and backgrounds. Despite their prevalence, warts can be a source of frustration and embarrassment for those affected. In this comprehensive blog, we'll delve into the world of warts, exploring their causes, types, treatment options, and preventive measures, empowering you to take control of these unwanted skin growths with confidence.
**Unraveling the Causes of Warts:**
Warts are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), a group of viruses that infect the top layer of the skin and mucous membranes. There are over 100 different strains of HPV, each with its own unique characteristics and preferred sites of infection. The most common types of warts include:
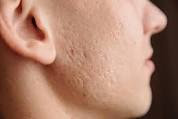
1. **Common Warts (Verruca Vulgaris):** Common warts typically appear as rough, raised bumps with a cauliflower-like texture. They often develop on the hands, fingers, and around the nails, but can also occur on other parts of the body.
2. **Plantar Warts:** Plantar warts are warts that develop on the soles of the feet, often in weight-bearing areas such as the heels or balls of the feet. They may appear as flat, rough lesions with black dots (petechiae) in the center, caused by small blood vessels that have become trapped within the wart.
3. **Flat Warts (Verruca Plana):** Flat warts are smooth, flat-topped lesions that typically occur in clusters on the face, neck, hands, or legs. They may be flesh-colored, pink, or slightly yellowish in appearance and can vary in size from a pinhead to a pencil eraser.
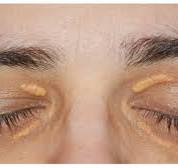
4. **Filiform Warts:** Filiform warts are long, narrow growths that protrude from the skin's surface, often resembling tiny fingers or threads. They commonly occur on the face, particularly around the eyes, nose, and mouth, as well as on the neck and under the chin.
**Identifying Risk Factors and Transmission:**
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing warts or make individuals more susceptible to infection. These risk factors include:
1. **Direct Contact:** Warts are highly contagious and can spread through direct contact with an infected person or contaminated surfaces. Sharing towels, razors, or other personal items with someone who has warts increases the risk of transmission.
2. **Weakened Immune System:** Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, organ transplant recipients, or individuals undergoing chemotherapy, are more susceptible to HPV infection and may be more prone to developing warts.
3. **Skin Trauma:** Skin trauma, such as cuts, scratches, or puncture wounds, can provide entry points for HPV to infect the skin and cause warts. People who bite their nails, pick at hangnails, or have damaged skin are at increased risk of developing warts.
4. **Warm, Moist Environments:** Warm, moist environments such as swimming pools, locker rooms, and communal showers provide ideal conditions for HPV transmission and wart development. Walking barefoot in these environments can increase the risk of contracting plantar warts.
**Exploring Treatment Options for Warts:**
While warts often resolve on their own without treatment, many individuals seek treatment to accelerate wart clearance, alleviate symptoms, and prevent transmission to others. Some common treatment options for warts include:
1. **Topical Treatments:** Over-the-counter and prescription topical treatments containing salicylic acid, podophyllin, or imiquimod can help dissolve wart tissue and stimulate the immune system's response to the virus. These treatments are typically applied directly to the wart and may require daily application for several weeks or months.
2. **Cryotherapy:** Cryotherapy involves freezing the wart with liquid nitrogen or another freezing agent to destroy the wart tissue. This procedure is typically performed in a healthcare provider's office and may require multiple sessions for complete wart clearance.
3. **Electrosurgery:** Electrosurgery, also known as curettage and electrodesiccation, involves using an electrical current to burn and scrape away the wart tissue. This procedure is performed under local anesthesia in a healthcare provider's office and may be effective for stubborn or recurring warts.
4. **Laser Therapy:** Laser therapy uses focused laser beams to destroy the blood vessels that supply the wart tissue, causing the wart to shrink and eventually fall off. Laser therapy is often used for warts that are resistant to other treatments or located in sensitive areas such as the face or genitals.
5. **Intralesional Immunotherapy:** Intralesional immunotherapy involves injecting a substance such as candida antigen or mumps virus antigen directly into the wart tissue to stimulate the immune system's response and promote wart clearance. This treatment may be used for recurrent or refractory warts that have not responded to other treatments.
**Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Strategies:**
Preventing warts involves adopting simple lifestyle strategies and practicing good hygiene habits to reduce the risk of HPV transmission and infection. Some preventive measures for avoiding warts include:
1. **Practice Good Hand Hygiene:** Wash your hands regularly with soap and water, especially after touching warts or coming into contact with potentially contaminated surfaces.
Avoid touching or picking at warts to prevent spreading the virus to other areas of the body.
2. **Keep Skin Dry and Clean:** Keep your skin clean and dry, particularly in warm, moist environments such as swimming pools or communal showers. Wear protective footwear in public areas to reduce the risk of contracting plantar warts.
3. **Avoid Sharing Personal Items:** Avoid sharing towels, razors, socks, or other personal items with others, especially if they have warts. Sharing personal items can spread the virus and increase the risk of HPV transmission.
4. **Protect Skin During Activities:** Wear gloves or protective clothing when engaging in activities that may expose the skin to HPV, such as gardening, yard work, or handling raw meat. Covering the skin can reduce the risk of skin trauma and subsequent wart development.
5. **Boost Immune Function:** Maintain a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management techniques to support optimal immune function. A strong immune system can help prevent HPV infection and reduce the likelihood of developing warts.
**Conclusion:**
Warts may be a common nuisance, but they need not control your life or diminish your confidence. With a better understanding of the causes, types, treatment options, and preventive measures for warts, you can take proactive steps to manage and minimize their impact on your skin and well-being. Whether seeking treatment for existing warts or adopting preventive measures to avoid future infections, know that help and support are available to guide you on your journey to wart-free skin.
Call now
on our Mobile 8669086098 to book an appointment
Kindly visit our website Derma Solutions to know more.
#warts #skingrowth #wart_treatment


Comments
Post a Comment