**Unlocking the Mysteries of Xanthelasma: Understanding, Treating, and Coping with Yellow Eyelid Deposits**
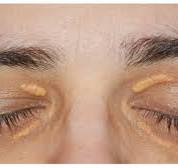
Xanthelasma, characterized by yellowish plaques or deposits on the eyelids, is a relatively common yet often misunderstood skin condition. While typically harmless, xanthelasma can be a source of concern and self-consciousness for those affected. In this enlightening blog, we'll delve into the world of xanthelasma, exploring its causes, symptoms, risk factors, treatment options, and strategies for coping with this distinctive dermatologic condition.
**Understanding Xanthelasma:**
Xanthelasma, derived from the Greek words "xanthos" (yellow) and "elasma" (plate), refers to yellowish plaques or deposits that develop on the eyelids. These deposits are composed of cholesterol, lipids, and other fatty substances, and they typically appear as soft, flat, or slightly raised lesions on the skin surrounding the eyes.
Xanthelasma lesions are usually painless and non-itchy, and they can vary in size from small, barely noticeable patches to larger, more prominent plaques. While xanthelasma can occur on any part of the eyelids, it most commonly affects the inner corners or upper eyelids.
**Causes and Risk Factors:**
The exact cause of xanthelasma is not fully understood, but several factors may contribute to its development, including:
1. **High Cholesterol Levels:** Xanthelasma is often associated with elevated levels of cholesterol and other lipids in the blood. The accumulation of cholesterol deposits in the skin around the eyes may result from underlying lipid disorders or metabolic abnormalities.
2. **Genetic Predisposition:** There appears to be a genetic component to xanthelasma, as the condition often runs in families. Individuals with a family history of xanthelasma or lipid disorders may be at increased risk of developing the condition.
3. **Age and Gender:** Xanthelasma tends to occur more frequently in middle-aged and older adults, particularly women. Hormonal changes associated with menopause or hormonal imbalances may contribute to the development of xanthelasma in some individuals.
4. **Underlying Medical Conditions:** Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, hypothyroidism, liver disease, and metabolic syndrome, may increase the risk of developing xanthelasma. These conditions can affect lipid metabolism and contribute to the formation of cholesterol deposits in the skin.
**Symptoms and Diagnosis:**
The primary symptom of xanthelasma is the presence of yellowish plaques or deposits on the eyelids. These lesions are typically asymptomatic but may cause cosmetic concerns or emotional distress due to their appearance.
Diagnosing xanthelasma usually involves a visual examination of the eyelids by a dermatologist or healthcare professional. In some cases, a biopsy or skin scraping may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other potential causes of eyelid lesions.
**Treatment Options:**
While xanthelasma itself is harmless and does not typically require treatment for medical reasons, many individuals seek treatment for cosmetic reasons or to alleviate concerns about their appearance. Several treatment options are available for managing xanthelasma, including:
1. **Topical Treatments:** Topical treatments such as trichloroacetic acid (TCA) or topical retinoids may be applied directly to the xanthelasma lesions to help reduce their size and appearance over time. These treatments work by promoting exfoliation and cell turnover, leading to gradual fading of the lesions.
2. **Cryotherapy:** Cryotherapy involves freezing the xanthelasma lesions using liquid nitrogen or another freezing agent. This causes the lesions to blister and peel off, resulting in smoother, clearer skin. Cryotherapy may be effective for smaller xanthelasma lesions but may require multiple sessions for optimal results.
3. **Laser Therapy:** Laser treatments, such as carbon dioxide (CO2) laser or pulsed-dye laser therapy, can be used to target and remove xanthelasma lesions with precision. Laser therapy works by selectively heating and vaporizing the cholesterol deposits, leaving surrounding skin tissue unharmed. Laser therapy may offer significant improvement in xanthelasma appearance with minimal scarring or downtime.
4. **Surgical Excision:** Surgical excision involves physically removing the xanthelasma lesions using a scalpel or surgical tool. This method is typically reserved for larger or more stubborn lesions and may be performed under local anesthesia in a dermatologist's office or outpatient setting. Surgical excision may result in scarring, so it's essential to discuss the risks and benefits with a healthcare professional before proceeding.
5. **Lipid-Lowering Medications:** In cases where xanthelasma is associated with elevated cholesterol levels or lipid disorders, lipid-lowering medications such as statins may be prescribed to help reduce cholesterol levels and prevent the recurrence of xanthelasma lesions. These medications work by inhibiting cholesterol synthesis and promoting the clearance of cholesterol from the bloodstream.
**Coping Strategies and Support:**
Living with xanthelasma can be challenging, particularly for individuals who experience self-consciousness or embarrassment about their appearance. Coping strategies and support resources can help individuals navigate the emotional and psychological aspects of living with xanthelasma, including:
1. **Education and Awareness:** Learning more about xanthelasma and its causes can help individuals better understand the condition and feel more empowered to seek treatment and support.
2. **Open Communication:** Talking openly and honestly with friends, family members, or healthcare providers about feelings and concerns related to xanthelasma can provide valuable emotional support and validation.
3. **Seeking Professional Help:** Consulting with a dermatologist or healthcare professional who specializes in skin conditions can offer personalized treatment options, advice, and support for managing xanthelasma.
4. **Support Groups:** Joining a support group or online community for individuals living with xanthelasma or similar skin conditions can provide a sense of belonging, camaraderie, and mutual support.
5. **Self-Care and Self-Compassion:** Practicing self-care activities such as meditation, mindfulness, or relaxation techniques can help reduce stress and promote emotional well-being. Cultivating self-compassion and self-acceptance can also foster resilience and confidence in coping with xanthelasma.
**Conclusion:**
Xanthelasma, while benign, can be a source of concern and self-consciousness for those affected. By understanding the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and coping strategies for xanthelasma, individuals can take proactive steps to manage the condition and improve their quality of life. Whether seeking treatment for cosmetic reasons or emotional support for coping with xanthelasma-related concerns, know that help and resources are available. With the guidance of healthcare professionals and the support of friends, family members, and community, individuals can navigate the journey of living with xanthelasma with confidence, resilience, and self-compassion.
Call now
on our Mobile 8669086098 to book an appointment
Kindly visit our website Derma Solutions to know more.
#yellow_eyelid_deposits #Xanthelasma #yellowish_plaques

Comments
Post a Comment