Unveiling Rosacea: Understanding Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Management
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that primarily affects the face, causing redness, visible blood vessels, bumps, and sometimes, thickened skin. It often develops gradually, with symptoms worsening over time, and can significantly impact a person's physical appearance and self-esteem. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the underlying causes of rosacea, explore its common symptoms, and discuss various management strategies to help individuals cope with and alleviate this chronic skin condition.
Causes of Rosacea:
Genetic Predisposition: Genetic factors play a significant role in the development of rosacea. Individuals with a family history of rosacea are more likely to inherit genetic traits that predispose them to the condition. Specific genetic variations related to immune system regulation, vascular function, and skin barrier integrity may contribute to rosacea susceptibility.
Immune System Dysfunction: Dysregulation of the immune system and chronic inflammation play key roles in the pathogenesis of rosacea. Abnormal immune responses to microbial triggers, such as Demodex mites and certain bacteria, can lead to persistent inflammation, vasodilation, and tissue damage in rosacea-affected skin.
Facial Redness (Erythema): Persistent facial redness, often described as flushing or blushing, is a hallmark symptom of rosacea. The redness typically affects the central face, including the cheeks, nose, forehead, and chin, and may worsen in response to triggers such as heat, sunlight, or spicy foods.
Visible Blood Vessels (Telangiectasia): Telangiectasia refers to the visible dilation of small blood vessels near the surface of the skin, resulting in the appearance of fine, red lines or spider veins. These blood vessels may be more prominent on the cheeks, nose, and chin in individuals with rosacea.
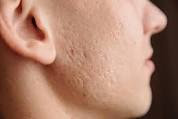
Papules and Pustules: Inflammatory papules and pustules, resembling acne lesions, may develop in rosacea-affected skin, particularly in the subtype known as papulopustular rosacea. These red, raised bumps may be tender or itchy and can persist for weeks to months, leading to scarring if left untreated.
Ocular Symptoms: Ocular rosacea involves inflammation of the eyes and eyelids, causing symptoms such as redness, dryness, itching, burning, tearing, and sensitivity to light. Ocular symptoms can range from mild irritation to more severe complications, such as corneal damage and vision impairment.
Thickened Skin (Phymatous Changes): In some cases, rosacea can lead to thickening and enlargement of the skin, particularly on the nose (rhinophyma), chin, forehead, or ears. Phymatous changes are more common in men and may be accompanied by irregular texture, prominent pores, and tissue overgrowth
Trigger Avoidance: Identifying and avoiding triggers that exacerbate rosacea symptoms is essential for disease management. Common triggers include sunlight, heat, spicy foods, alcohol, caffeine, stress, and certain skincare products. Keeping a trigger diary can help individuals pinpoint specific factors that worsen their symptoms.
Skincare Regimen: Gentle skincare practices are crucial for individuals with rosacea-prone skin. This includes using mild, non-irritating cleansers and moisturizers, avoiding abrasive scrubs and exfoliants, and opting for fragrance-free, hypoallergenic products. Sun protection is also essential, with daily use of broad-spectrum sunscreen and protective clothing.
Topical Treatments: Topical medications, such as metronidazole, azelaic acid, and sodium sulfacetamide-sulfur, are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation, redness, and papules and pustules associated with rosacea. These medications are applied directly to the affected areas once or twice daily and may take several weeks to show noticeable improvement.
Oral Medications: Oral antibiotics, such as doxycycline, minocycline, and tetracycline, are frequently prescribed for their anti-inflammatory properties and ability to suppress bacterial overgrowth associated with rosacea. In severe or refractory cases, oral isotretinoin may be considered to target both inflammatory and sebaceous gland activity.
Laser and Light Therapies: Laser and light-based therapies, such as intense pulsed light (IPL) and pulsed dye laser (PDL) treatments, can effectively reduce facial redness, visible blood vessels, and certain types of rosacea lesions. These non-invasive procedures target blood vessels and inflammation in the skin while sparing surrounding tissues.
To know more about Dr. Amey Kelkar visit our website Derma Solutions



Comments
Post a Comment