Understanding Acne and Pimples: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments
Acne and pimples are common skin conditions that affect millions of people worldwide, regardless of age, gender, or ethnicity. While often considered a teenage woe, acne can persist well into adulthood, causing physical discomfort, emotional distress, and even scarring. In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the root causes of acne and pimples, explore their symptoms, and discuss various treatment options to help you achieve clearer, healthier skin.
Causes of Acne and Pimples:
Hormonal Imbalance: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause, can trigger excess oil production (sebum) in the skin's sebaceous glands. This surplus oil, combined with dead skin cells and bacteria, can clog pores, leading to acne breakouts.
Genetics: A person's genetic predisposition plays a significant role in their susceptibility to acne. If one or both parents experienced acne during their lifetime, their offspring are more likely to develop similar skin issues.
Poor Skincare Habits: Inadequate skincare routines, such as infrequent cleansing, using harsh products, or failing to remove makeup before bed, can exacerbate acne by allowing dirt, oil, and bacteria to accumulate on the skin's surface.
Diet: While the link between diet and acne isn't fully understood, certain foods, such as those high in sugar, refined carbohydrates, and dairy, may contribute to acne development in some individuals. Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help maintain clearer skin.
Stress: Chronic stress can trigger hormonal imbalances and inflammation in the body, which may worsen existing acne or precipitate new breakouts. Incorporating stress-reduction techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, can help mitigate its impact on skin health.
Symptoms of Acne and Pimples:
Whiteheads: Closed comedones, or whiteheads, appear as small, flesh-colored bumps with a white or yellowish center. They occur when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells, trapping them beneath the skin's surface.
Blackheads: Open comedones, or blackheads, are similar to whiteheads but have a dark or black appearance due to oxidation of the trapped debris. They often appear on the nose, chin, and forehead and are easily identifiable by their darkened tops.
Papules: Papules are small, inflamed bumps that develop on the skin's surface. They may feel tender to the touch and appear red or pink in color. Papules occur when the walls of hair follicles become ruptured, leading to inflammation and swelling.
Pustules: Pustules are pus-filled lesions characterized by a white or yellow center surrounded by red, inflamed skin. They are often painful and may be accompanied by tenderness and swelling. Pustules develop when bacterial infection exacerbates existing inflammation within the hair follicles.
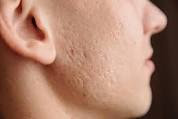
Nodules and Cysts: Nodular and cystic acne are severe forms of acne characterized by large, painful lesions deep within the skin. Nodules are hard, inflamed bumps that develop beneath the skin's surface, while cysts are pus-filled lesions that can cause significant scarring if left untreated.
Treatments for Acne and Pimples:
Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter (OTC) topical treatments containing ingredients such as benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, and retinoids can help unclog pores, reduce inflammation, and promote cell turnover. Prescription-strength formulations may be recommended for severe or persistent acne.
Oral Medications: Oral antibiotics, such as tetracycline, doxycycline, and minocycline, are commonly prescribed to combat bacterial overgrowth and reduce inflammation associated with moderate to severe acne. Oral contraceptives containing estrogen and progestin can help regulate hormone levels and improve acne in some women.
Isotretinoin: Isotretinoin, also known as Accutane, is a potent oral medication reserved for severe, treatment-resistant acne. It works by reducing sebum production, shrinking oil glands, and preventing the formation of acne-causing bacteria. Due to its potential side effects, including birth defects and liver damage, isotretinoin use requires close monitoring by a healthcare professional.
Light Therapy: Phototherapy techniques, such as blue light therapy and photodynamic therapy (PDT), utilize specific wavelengths of light to target acne-causing bacteria, reduce inflammation, and promote skin healing. These non-invasive treatments are often used in conjunction with other acne therapies for enhanced efficacy.
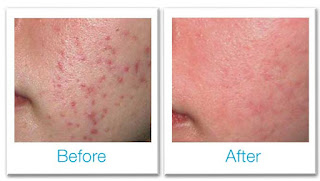
Chemical Peels: Chemical peels involve the application of a chemical solution to the skin, which causes exfoliation of the outermost layer and stimulates cell turnover. By removing dead skin cells and unclogging pores, chemical peels can improve acne, diminish acne scars, and enhance overall skin texture and tone.
Conclusion: Acne and pimples are multifactorial skin conditions influenced by genetics, hormones, lifestyle factors, and environmental triggers. While they can be frustrating to manage, numerous treatment options are available to help individuals achieve clearer, healthier skin. By understanding the underlying causes of acne, recognizing its symptoms, and exploring effective treatment modalities, you can take proactive steps towards achieving a smoother, blemish-free complexion and boosting your confidence and self-esteem. Remember to consult with a dermatologist or skincare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs and concerns. With patience, consistency, and proper care, clearer skin is within reach for everyone.
Call now on our Mobile 8669086098 for booking an appointment
To know more about Dr. Amey Kelkar visit our website Derma Solutions



Comments
Post a Comment