Decoding Psoriasis: Understanding Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments
Causes of Psoriasis:
Genetic Predisposition:
Genetic factors play a significant role in the development of psoriasis. Individuals with a family history of psoriasis are more likely to inherit genetic mutations that predispose them to the condition. Specific genes associated with immune system regulation, such as HLA-C and IL-23R, have been implicated in psoriasis susceptibility.
Immune System Dysfunction:
Psoriasis is considered an autoimmune disorder, where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, triggering inflammation and abnormal skin cell proliferation. T cells, a type of white blood cell, play a central role in driving the inflammatory response observed in psoriatic lesions.
Environmental Triggers:
Environmental factors, such as infections, trauma, stress, and certain medications, can exacerbate or trigger psoriasis flare-ups in susceptible individuals. Common triggers include streptococcal throat infections, injury to the skin (Koebner phenomenon), emotional stress, and certain medications, such as beta-blockers and lithium.
Lifestyle Factors:
Lifestyle choices, such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, and poor dietary habits, may influence psoriasis development and severity. Smoking, in particular, has been associated with an increased risk of psoriasis onset and more severe disease manifestations.
Psychological Factors:
Psychological stress and emotional factors, such as anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem, can exacerbate psoriasis symptoms and trigger flare-ups. Stress management techniques, such as relaxation therapy, mindfulness meditation, and counseling, may help improve psoriasis outcomes and enhance overall well-being.
Symptoms of Psoriasis:
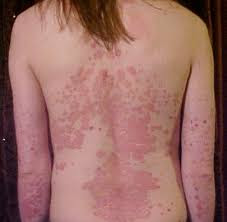
Red, Inflamed Patches (Plaques):
The most common symptom of psoriasis is the appearance of red, inflamed patches of skin covered with silvery-white scales. These plaques typically occur on the elbows, knees, scalp, lower back, and other areas of friction or trauma.
Itching and Discomfort:
Psoriatic plaques can be accompanied by itching, burning, or stinging sensations, causing significant discomfort and irritation. Scratching or picking at the affected areas can worsen symptoms and lead to secondary infections.
Thickened or Pitted Nails:
Psoriasis can affect the nails, causing changes in texture, color, and shape. Affected nails may become thickened, discolored, brittle, or pitted, leading to nail separation or crumbling.
Scalp Psoriasis:
Psoriasis can also affect the scalp, causing red, scaly patches and dandruff-like flakes. Scalp psoriasis may extend beyond the hairline onto the forehead, neck, and ears, leading to embarrassment and self-consciousness.
Psoriatic Arthritis:
In some cases, psoriasis can be associated with psoriatic arthritis, a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the joints and connective tissues. Psoriatic arthritis can cause joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and deformities, significantly impacting mobility and quality of life.
Treatments for Psoriasis:
Topical Treatments:
Topical medications, such as corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, retinoids, and calcineurin inhibitors, are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation, normalize skin cell turnover, and alleviate symptoms of mild to moderate psoriasis.
Phototherapy (Light Therapy):
Phototherapy involves exposing the skin to controlled doses of ultraviolet (UV) light to suppress immune responses, reduce inflammation, and promote healing of psoriatic lesions. Narrowband UVB therapy and PUVA (psoralen plus UVA) therapy are effective phototherapy modalities for psoriasis treatment.
Systemic Medications:
Systemic medications, such as oral retinoids, methotrexate, cyclosporine, and biologic agents (e.g., TNF-alpha inhibitors, IL-17 inhibitors, IL-23 inhibitors), are reserved for severe or refractory cases of psoriasis that do not respond adequately to topical treatments or phototherapy.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Adopting healthy lifestyle habits, such as quitting smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy weight, and following a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, may help reduce psoriasis severity and improve overall skin health.
Stress Management:
Stress management techniques, such as relaxation therapy, mindfulness meditation, yoga, and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can help reduce psychological stress and emotional triggers that exacerbate psoriasis symptoms.
Conclusion:
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by the rapid overproduction of skin cells, leading to the formation of red, inflamed patches covered with silvery-white scales. While there is no cure for psoriasis, various treatment options are available to help manage symptoms, alleviate discomfort, and improve overall quality of life. By understanding the underlying causes of psoriasis, recognizing its common symptoms, and exploring effective treatment modalities, individuals with psoriasis can take proactive steps towards achieving clearer, healthier skin and better disease control. It's essential to work closely with a dermatologist or healthcare professional to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to individual needs and preferences. With proper care, support, and adherence to treatment recommendations, individuals with psoriasis can achieve long-term symptom relief and enjoy a better quality of life.
Call now
on our Mobile 8669086098 for booking an appointment
To know
more about Dr. Amey Kelkar visit our website Derma Solutions

Comments
Post a Comment